Calibration in pharmaceutical industry

What is Data Integrity? Why is it important and acute? What could a breach cause? What is ALCOA Plus?
As a concept, data integrity is by no means a new one, it has been around for several decades. Anyhow, in this article, we look at the data integrity more from the calibration process point of view, and focus mainly on the pharmaceutical and regulated industry. At first we take a look at the data integrity generally; what it is, why it is important and what a breach could cause. The ALCOA plus concept is also briefly discussed.
I remember in the early 90’s when we had pharmaceutical customers auditing us prior to a calibration software purchase, and data integrity was already then one of the normal topics discussed during such a supplier audit. So it is not a new topic, although it has become more acute recently.
Download the related free white paper by clicking the picture below:
It’s all about trust
Often, when we buy an everyday product, we can quickly see if the product is operating properly, or if it is faulty. For example, if you buy a new TV and turn it on, you can quickly see if it working or not. But with different products it is not so easy to see if you have a proper product. This is especially the case with medicines. When you pick up a medicine, how do know that it is a product working properly according to design specifications? In most cases you can’t tell that, so it is all about trust – you must be able to trust that the medicine you take is a proper one.
What is Data Integrity?
Data integrity is fundamental in a pharmaceutical quality system ensuring that products are of the required quality.
In every process, there is a lot of data produced. Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of the accuracy and consistency of the data over its entire life-cycle. It is a critical aspect to the design, implementation and usage of any system which stores, processes, or retrieves data. The term Data Integrity is pretty widely used and has different meanings in different contexts. The term itself is pretty old and was initially used in computing. The integrity of the data collected and recorded by pharmaceutical manufacturers is critical to ensuring that high quality and safe products are produced. To ensure the integrity of data, it should be protected from accidental or intentional modifications, falsification and deletion.
With many processes in the process industry, you cannot just simply test the final product to see if it is a proper one. Instead you must assure that the conditions during the process are correct in order for it to produce the correct product. These critical conditions must naturally be recorded and maintained to assure they were correct. This is certainly the case in many processes in a pharmaceutical plant.
Why is Data Integrity important at the moment?
Data integrity has recently risen to an even more important topic than before.
Data integrity related violations have led to several regulatory actions such as warning letters and import alerts. Actually, a large number of the recent warning letters issued by FDA are somehow related to data integrity.
As international regulatory agencies have more focus on data integrity, the FDA, WHOA and MHRA auditors have been trained to better recognize data integrity issues.
MHRA (Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency in UK) has recently released new guide “GMP Data Integrity Definitions and Guidance for Industry” (March 2015). There is a deadline set for pharmaceutical companies to comply at the end of 2017. Also, FDA has released “Data Integrity and Compliance With CGMP - Guidance for Industry” (April 2016). This is still in draft mode but has been on comment rounds. Both of these will naturally have effect with the pharmaceutical industry. Sure already before there has been guidance for the good manufacturing practice (CGMP), such as 21 CFR parts (210, 211, and 212), discussing data integrity related issues, but these mentioned new regulation updates will raise the focus.
One additional reason why more focus has been put to data integrity is the increase of the use of mobile devices in calibration processes. This includes applications used in tablets and mobile phones. It also includes the increase of the use of documenting calibrators, which automatically store the calibration results in their memory during a calibration and transfer this data to calibration software. Since the use of automated documenting calibrators will improve the business case of a calibration system, they are being more widely used. To learn more on what a documenting calibrator is and how it benefits the calibration process, please check the earlier blog post: What is a documenting calibrator and how do you benefit from using one?
As results of all these, data integrity is getting more and more acute.
Impacts of breach of data integrity
The impact of breach of data integrity can be looked as the impact to customer and impact to the pharmaceutical company.
For the customer the impact can be that the medicine does not have the required effect, patient safety can be compromised and in a worst case it can cause even loss of lives.
For the pharmaceutical company the impact can be; warning letter from FDA, bans of license to produce, negative reputation, loss of customer confidence, reduction of market share, and reduction of share price.
So the impacts of breach of data integrity may be huge.
Accidental / intentional
A breach of data integrity may be accidental or intentional. Often there are computerized systems involved to handle the data and the users may not be aware of any issues in such systems. Certainly the majority of data integrity issues are accidental and non-intentional. Anyhow, in looking at some of the FDA warning letters, we can see that in the very worst cases there has been even intentional falsifying of records.
Main steps towards better data integrity
Many pharmaceutical companies seems to agree that the main steps towards better data integrity are:
- Better education and communication
- Detection and mitigation of risks
- Focus on technology and IT systems
- Governance of data integrity
ALCOA and ALCOA plus
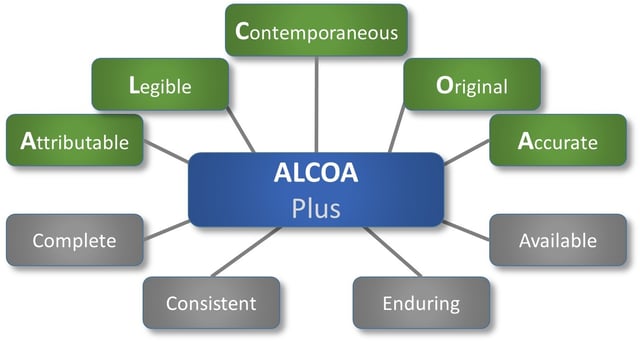
The acronym ALCOA has been around since the 1990’s, being used by regulated industries as a framework for ensuring data integrity, and is key to good documentation practice (GDP). ALCOA relates to data, whether paper or electronic, and is defined by FDA guidance as:
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate
The newer ALCOA Plus ads a few attributes to the list:
- Complete
- Consistent
- Enduring
- Available
For more detailed description of the ALCOA Plus, please take a look at the related free white paper.
What could cause data integrity issues?
Some practical and very general things that could cause data integrity issues in any systems are, for example: lack of training, user privileges, poor or shared passwords, control of a computerized system, incomplete data entry, and lack of audit data records for changes and modifications.
The first trap to avoid for consumers – fraud drugs
Although not really a data integrity issues for the industry, this is an important point for consumers. People are buying more from the internet nowadays and you can also buy medicines from internet, but unfortunately you don’t always get what you ordered. A huge amount of medicines bought online are frauds. Sometimes packaging is obviously inappropriate, so it becomes apparent that the medication is a fraud. But, unfortunately that is not always the case and people do, at times, consume fraudulent medicine. It is clear that the fraud medication does not provide the expected cure, but it is also a big risk for our safety and as at its worse, it may be even lethal.
New regulation for product packaging to avoid fraud drugs
To better control fraud drugs, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has recently introduced a new regulation that will require all prescription drug makers in all (but three) EU (European Union) countries to incorporate new safety features on their product packaging by February 2019. The regulation, which is part of a broader effort to combat falsified medicines in the EU, will require drug makers to add a unique identifier and an anti-tampering device to the packaging of most centrally authorized products. This naturally ads another burden and cost for the drug manufacturers, to build the systems to support this, but this will certainly be beneficial for the customers. Although this specific regulation is for the European Union area, it will have effect globally.
Conclusion
Although the data integrity concept has existed for a long time, it has recently risen to be more acute due to the use of mobile tools and added focus of regulatory agencies. Although in the end, data integrity is pretty common sense - to assure the integrity of data throughout its life cycle - in practice with various systems and tools being used, it gets more complicated. Since the impacts of the breach of data integrity can be enormous, it is something that has a high priority.
In another blog post later on, I will take look into more practical things, such as what can cause data integrity issues in a normal process calibration environment, whether it is a paper based or paperless system, insourced or outsourced.
Related Beamex products
Using the Beamex MC6 documenting calibrator with the “Security Plus” optional feature ensures the integrity of the calibration data throughout the calibration process, when used in conjunction with the Beamex CMX calibration management software.
Related useful references
21 CFR Part 11, Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures:
http://www.fda.gov/RegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm125067.htm
MHRA GMP Data Integrity Definitions and Guidance for Industry, March 2015:
https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/412735/Data_integrity_definitions_and_guidance_v2.pdf
Data Integrity and Compliance with CGMP Guidance for Industry DRAFT GUIDANCE, April 2016:
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm495891.pdf
FDA warning letters are public and can be found here:
http://www.fda.gov/ICECI/EnforcementActions/WarningLetters/default.htm
European Medicines Agency (EMA), recent regulation for product packaging:
http://www.raps.org/Regulatory-Focus/News/2016/02/09/24281/EU-Regulation-Requires-New-Safety-Features-on-Drug-Packaging-by-2019/








.png)









.jpg)



Discussion